dbt Cloud release notes
dbt Cloud release notes for recent and historical changes. Release notes fall into one of the following categories:
- New: New products and features
- Enhancement: Performance improvements and feature enhancements
- Fix: Bug and security fixes
- Behavior change: A change to existing behavior that doesn't fit into the other categories, such as feature deprecations or changes to default settings
Release notes are grouped by month for both multi-tenant and virtual private cloud (VPC)* environments
* The official release date for this new format of release notes is May 15th, 2024. Historical release notes for prior dates may not reflect all available features released earlier this year or their tenancy availability.
October 2024
- Enhancement: In dbt Cloud Versionless, snapshots defined in SQL files can now use
configdefined inschema.ymlYAML files. This update resolves the previous limitation that required snapshot properties to be defined exclusively indbt_project.ymland/or aconfig()block within the SQL file. This enhancement will be included in the upcoming dbt Core v1.9 release. - Enhancement: In May 2024, dbt Cloud versionless began inferring a model's
primary_keybased on configured data tests and/or constraints withinmanifest.json. The inferredprimary_keyis visible in dbt Explorer and utilized by the dbt Cloud compare changes feature. This will also be released in dbt Core 1.9. Read about the order dbt infers columns can be used as primary key of a model. - New: dbt Explorer now includes trust signal icons, which is currently available as a Preview. Trust signals offer a quick, at-a-glance view of data health when browsing your dbt models in Explorer. These icons indicate whether a model is Healthy, Caution, Degraded, or Unknown. For accurate health data, ensure the resource is up-to-date and has had a recent job run. Refer to Trust signals for more information.
- New: Auto exposures are now available in Preview in dbt Cloud. Auto-exposures helps users understand how their models are used in downstream analytics tools to inform investments and reduce incidents. It imports and auto-generates exposures based on Tableau dashboards, with user-defined curation. To learn more, refer to Auto exposures.
September 2024
- New: Use the new recommended syntax for defining
foreign_keyconstraints usingrefs, available in dbt Cloud Versionless. This will soon be released in dbt Core v1.9. This new syntax will capture dependencies and works across different environments. - Enhancement: You can now run Semantic Layer commands commands in the dbt Cloud IDE. The supported commands are
dbt sl list,dbt sl list metrics,dbt sl list dimension-values,dbt sl list saved-queries,dbt sl query,dbt sl list dimensions,dbt sl list entities, anddbt sl validate. - New: Microsoft Excel, a dbt Semantic Layer integration, is now generally available. The integration allows you to connect to Microsoft Excel to query metrics and collaborate with your team. Available for Excel Desktop or Excel Online. For more information, refer to Microsoft Excel.
- New: Data health tile is now generally available in dbt Explorer. Data health tiles provide a quick at-a-glance view of your data quality, highlighting potential issues in your data. You can embed these tiles in your dashboards to quickly identify and address data quality issues in your dbt project.
- New: dbt Explorer's Model query history feature is now in Preview for dbt Cloud Enterprise customers. Model query history allows you to view the count of consumption queries for a model based on the data warehouse's query logs. This feature provides data teams insight, so they can focus their time and infrastructure spend on the worthwhile used data products. To learn more, refer to Model query history.
- Enhancement: You can now use Extended Attributes and Environment Variables when connecting to the Semantic Layer. If you set a value directly in the Semantic Layer Credentials, it will have a higher priority than Extended Attributes. When using environment variables, the default value for the environment will be used. If you're using exports, job environment variable overrides aren't supported yet, but they will be soon.
- New: There are two new environment variable defaults —
DBT_CLOUD_ENVIRONMENT_NAMEandDBT_CLOUD_ENVIRONMENT_TYPE. - New: The Amazon Athena warehouse connection is available as a public preview for dbt Cloud accounts that have upgraded to
versionless.
August 2024
- Fix: Fixed an issue in dbt Explorer where navigating to a consumer project from a public node resulted in displaying a random public model rather than the original selection.
- New: You can now configure metrics at granularities at finer time grains, such as hour, minute, or even by the second. This is particularly useful for more detailed analysis and for datasets where high-resolution time data is required, such as minute-by-minute event tracking. Refer to dimensions for more information about time granularity.
- Enhancement: Microsoft Excel now supports saved selections and saved queries. Use Saved selections to save your query selections within the Excel application. The application also clears stale data in trailing rows by default. To return your results and keep any previously selected data intact, un-select the Clear trailing rows option.
- Behavior change: GitHub is no longer supported for OAuth login to dbt Cloud. Use a supported SSO or OAuth provider to securely manage access to your dbt Cloud account.
July 2024
-
Behavior change:
target_schemais no longer a required configuration for snapshots. You can now target different schemas for snapshots across development and deployment environments using the schema config. -
New: Connections are now available under Account settings as a global setting. Previously, they were found under Project settings. This is being rolled out in phases over the coming weeks.
-
New: Admins can now assign environment-level permissions to groups for specific roles.
-
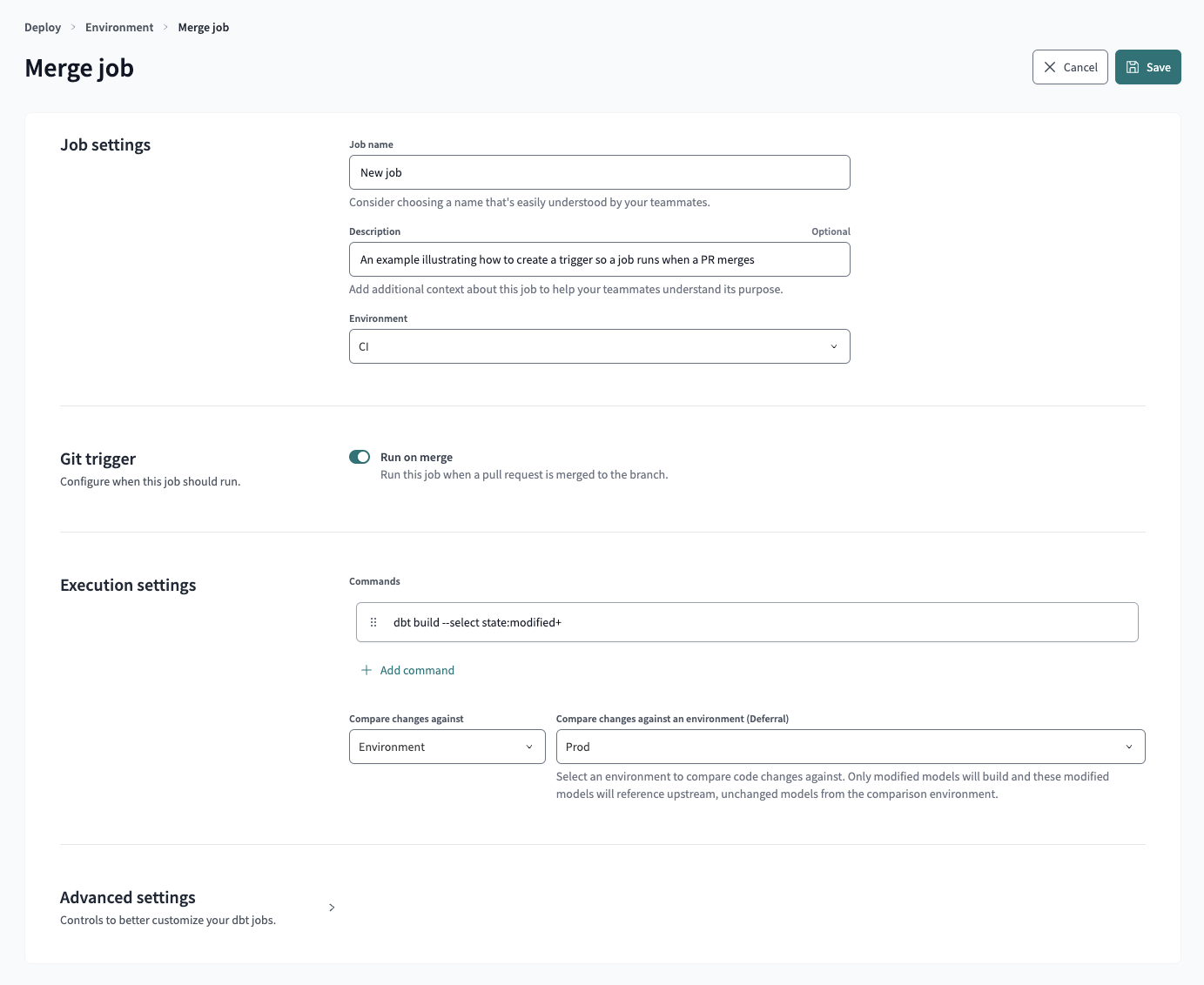
New: Merge jobs for implementing continuous deployment (CD) workflows are now GA in dbt Cloud. Previously, you had to either set up a custom GitHub action or manually build the changes every time a pull request is merged.
-
New: The ability to lint your SQL files from the dbt Cloud CLI is now available. To learn more, refer to Lint SQL files.
-
Behavior change: dbt Cloud IDE automatically adds a
--limit 100to preview queries to avoid slow and expensive queries during development. Recently, dbt Core changed how thelimitis applied to ensure thatorder byclauses are consistently respected. Because of this, queries that already contain a limit clause might now cause errors in the IDE previews. To address this, dbt Labs plans to provide an option soon to disable the limit from being applied. Until then, dbt Labs recommends removing the (duplicate) limit clause from your queries during previews to avoid these IDE errors. -
Enhancement: Introducing a revamped overview page for dbt Explorer, available in beta. It includes a new design and layout for the Explorer homepage. The new layout provides a more intuitive experience for users to navigate their dbt projects, as well as a new Latest updates section to view the latest changes or issues related to project resources. To learn more, refer to Overview page.
dbt Semantic Layer
- New: Introduced the
dbt-sl-sdkPython software development kit (SDK) Python library, which provides you with easy access to the dbt Semantic Layer with Python. It allows developers to interact with the dbt Semantic Layer APIs and query metrics and dimensions in downstream tools. Refer to the dbt Semantic Layer Python SDK for more information. - New: Introduced Semantic validations in CI pipelines. Automatically test your semantic nodes (metrics, semantic models, and saved queries) during code reviews by adding warehouse validation checks in your CI job using the
dbt sl validatecommand. You can also validate modified semantic nodes to guarantee code changes made to dbt models don't break these metrics. Refer to Semantic validations in CI to learn about the additional commands and use cases. - New: We now expose the
metafield within the config property for dbt Semantic Layer metrics in the JDBC and GraphQL APIs under themetafield. - New: Added a new command in the dbt Cloud CLI called
export-all, which allows you to export multiple or all of your saved queries. Previously, you had to explicitly specify the list of saved queries. - Enhancement: The dbt Semantic Layer now offers more granular control by supporting multiple data platform credentials, which can represent different roles or service accounts. Available for dbt Cloud Enterprise plans, you can map credentials to service tokens for secure authentication. Refer to Set up dbt Semantic Layer for more details.
- Fix: Addressed a bug where unicode query filters (such as Chinese characters) were not working correctly in the dbt Semantic Layer Tableau integration.
- Fix: Resolved a bug with parsing certain private keys for BigQuery when running an export.
- Fix: Addressed a bug that caused a "closed connection" error to be returned when querying or running an Export.
- Fix: Resolved an issue in dbt Core where, during partial parsing, all generated metrics in a file were incorrectly deleted instead of just those related to the changed semantic model. Now, only the metrics associated with the modified model are affected.
June 2024
-
New: Introduced new granularity support for cumulative metrics in MetricFlow. Granularity options for cumulative metrics are slightly different than granularity for other metric types. For other metrics, we use the
date_truncfunction to implement granularity. However, because cumulative metrics are non-additive (values can't be added up), we can't use thedate_truncfunction to change their time grain granularity.Instead, we use the
first(),last(), andavg()aggregation functions to aggregate cumulative metrics over the requested period. By default, we take the first value of the period. You can change this behavior by using theperiod_aggparameter. For more information, refer to Granularity options for cumulative metrics.
dbt Semantic Layer
- New: Added support for Predicate pushdown SQL optimization in MetricFlow. We will now push down categorical dimension filters to the metric source table. Previously filters were applied after we selected from the metric source table. This change helps reduce full table scans on certain query engines.
- New: Enabled
wherefilters on dimensions (included in saved queries) to use the cache during query time. This means you can now dynamically filter your dashboards without losing the performance benefits of caching. Refer to caching for more information. - Enhancement: In Google Sheets, we added information icons and descriptions to metrics and dimensions options in the Query Builder menu. Click on the Info icon button to view a description of the metric or dimension. Available in the following Query Builder menu sections: metric, group by, where, saved selections, and saved queries.
- Enhancement: In Google Sheets, you can now apply granularity to all time dimensions, not just metric time. This update uses our APIs to support granularity selection on any chosen time dimension.
- Enhancement: Improved querying error message when no semantic layer credentials were set.
- Enhancement: Querying grains for cumulative metrics now returns multiple granularity options (day, week, month, quarter, year) like all other metric types. Previously, you could only query one grain option for cumulative metrics.
- Fix: Removed errors that prevented querying cumulative metrics with other granularities.
- Fix: Fixed various Tableau errors when querying certain metrics or when using calculated fields.
- Fix: In Tableau, we relaxed naming field expectations to better identify calculated fields.
- Fix: Fixed an error when refreshing database metadata for columns that we can't convert to Arrow. These columns will now be skipped. This mainly affected Redshift users with custom types.
- Fix: Fixed Private Link connections for Databricks.
Also available this month:
- Enhancement: Updates to the UI when creating merge jobs are now available. The updates include improvements to helper text, new deferral settings, and performance improvements.
- New: The dbt Semantic Layer now offers a seamless integration with Microsoft Excel, available in preview. Build semantic layer queries and return data on metrics directly within Excel, through a custom menu. To learn more and install the add-on, check out Microsoft Excel.
- New: Job warnings are now GA. Previously, you could receive email or Slack alerts about your jobs when they succeeded, failed, or were canceled. Now with the new Warns option, you can also receive alerts when jobs have encountered warnings from tests or source freshness checks during their run. This gives you more flexibility on when to be notified.
- New: A preview of the dbt Snowflake Native App is now available. With this app, you can access dbt Explorer, the Ask dbt chatbot, and orchestration observability features, extending your dbt Cloud experience into the Snowflake UI. To learn more, check out About the dbt Snowflake Native App and Set up the dbt Snowflake Native App.
May 2024
- Enhancement: We've now introduced a new Prune branches Git button in the dbt Cloud IDE. This button allows you to delete local branches that have been deleted from the remote repository, keeping your branch management tidy. Available in all regions now and will be released to single tenant accounts during the next release cycle.
dbt Cloud Launch Showcase event
The following features are new or enhanced as part of our dbt Cloud Launch Showcase event on May 14th, 2024:
-
New: dbt Assist is a powerful AI feature helping you generate documentation and tests, saving you time as you deliver high-quality data. Available in private beta for a subset of dbt Cloud Enterprise users and in the dbt Cloud IDE. Register your interest to join the private beta.
-
New: The new low-code editor, now in private beta, enables less SQL-savvy analysts to create or edit dbt models through a visual, drag-and-drop experience inside of dbt Cloud. These models compile directly to SQL and are indistinguishable from other dbt models in your projects: they are version-controlled, can be accessed across projects in dbt Mesh, and integrate with dbt Explorer and the Cloud IDE. Register your interest to join the private beta.
-
New: dbt Cloud CLI is now Generally Available (GA) to all users. The dbt Cloud CLI is a command-line interface that allows you to interact with dbt Cloud, use automatic deferral, leverage dbt Mesh, and more!
-
New: The VS Code extension Power user for dbt Core and dbt Cloud is now available in beta for dbt Cloud CLI users. The extension accelerates dbt and SQL development and includes features such as generating models from your source definitions or SQL, and more!
-
New: Unit tests are now GA in dbt Cloud. Unit tests enable you to test your SQL model logic against a set of static inputs.
-
New: MetricFlow enables you to now add metrics as dimensions to your metric filters to create more complex metrics and gain more insights. Available for all dbt Cloud Semantic Layer users.
-
New: Staging environment is now GA. Use staging environments to grant developers access to deployment workflows and tools while controlling access to production data. Available to all dbt Cloud users.
-
New: Oauth login support via Databricks is now GA to Enterprise customers.
-
New: Native support for Microsoft Fabric in dbt Cloud is now GA. This feature is powered by the dbt-fabric adapter. To learn more, refer to Connect Microsoft Fabric and Microsoft Fabric DWH configurations. There's also a quickstart guide to help you get started.
-
New: dbt Mesh is now GA to dbt Cloud Enterprise users. dbt Mesh is a framework that helps organizations scale their teams and data assets effectively. It promotes governance best practices and breaks large projects into manageable sections. Get started with dbt Mesh by reading the dbt Mesh quickstart guide.
-
New: The dbt Semantic Layer Tableau Desktop, Tableau Server, and Google Sheets integration is now GA to dbt Cloud Team or Enterprise accounts. These first-class integrations allow you to query and unlock valuable insights from your data ecosystem.
-
Enhancement: As part of our ongoing commitment to improving the dbt Cloud IDE, the filesystem now comes with improvements to speed up dbt development, such as introducing a Git repository limit of 10GB.
Also available this month:
-
Update: The dbt Cloud CLI is now available for Azure single tenant and is accessible in all deployment regions for both multi-tenant and single-tenant accounts.
-
New: The dbt Semantic Layer introduces declarative caching, allowing you to cache common queries to speed up performance and reduce query compute costs. Available for dbt Cloud Team or Enterprise accounts.
-
Behavior change: Introduced the
require_resource_names_without_spacesflag, opt-in and disabled by default. If set toTrue, dbt will raise an exception if it finds a resource name containing a space in your project or an installed package. This will become the default in a future version of dbt. Read No spaces in resource names for more information.
April 2024
-
Behavior change: Introduced the
require_explicit_package_overrides_for_builtin_materializationsflag, opt-in and disabled by default. If set toTrue, dbt will only use built-in materializations defined in the root project or within dbt, rather than implementations in packages. This will become the default in May 2024 (dbt Core v1.8 and "Versionless" dbt Cloud). Read Package override for built-in materialization for more information.
dbt Semantic Layer
- New: Use Saved selections to save your query selections within the Google Sheets application. They can be made private or public and refresh upon loading.
- New: Metrics are now displayed by their labels as
metric_name. - Enhancement: Metrics now supports the
metaoption under the config property. Previously, we only supported the now deprecatedmetatag. - Enhancement: In the Google Sheets application, we added support to allow jumping off from or exploring MetricFlow-defined saved queries directly.
- Enhancement: In the Google Sheets application, we added support to query dimensions without metrics. Previously, you needed a dimension.
- Enhancement: In the Google Sheets application, we added support for time presets and complex time range filters such as "between", "after", and "before".
- Enhancement: In the Google Sheets application, we added supported to automatically populate dimension values when you select a "where" filter, removing the need to manually type them. Previously, you needed to manually type the dimension values.
- Enhancement: In the Google Sheets application, we added support to directly query entities, expanding the flexibility of data requests.
- Enhancement: In the Google Sheets application, we added an option to exclude column headers, which is useful for populating templates with only the required data.
- Deprecation: For the Tableau integration, the
METRICS_AND_DIMENSIONSdata source has been deprecated for all accounts not actively using it. We encourage users to transition to the "ALL" data source for future integrations.
March 2024
- New: The Semantic Layer services now support using Privatelink for customers who have it enabled.
- New: You can now develop against and test your Semantic Layer in the Cloud CLI if your developer credential uses SSO.
- Enhancement: You can select entities to Group By, Filter By, and Order By.
- Fix:
dbt parseno longer shows an error when you use a list of filters (instead of just a string filter) on a metric. - Fix:
join_to_timespinenow properly gets applied to conversion metric input measures. - Fix: Fixed an issue where exports in Redshift were not always committing to the DWH, which also had the side-effect of leaving table locks open.
- Behavior change: Introduced the
source_freshness_run_project_hooksflag, opt-in and disabled by default. If set toTrue, dbt will includeon-run-*project hooks in thesource freshnesscommand. This will become the default in a future version of dbt. Read Project hooks with source freshness for more information.
February 2024
-
New: Exports allow you to materialize a saved query as a table or view in your data platform. By using exports, you can unify metric definitions in your data platform and query them as you would any other table or view.
-
New: You can access a list of your exports with the new list saved-queries command by adding
--show-exports -
New: The dbt Semantic Layer and Tableau Connector now supports relative date filters in Tableau.
-
Enhancement: The dbt Semantic Layer Google Sheets integration now exposes a note on the cell where the data was requested, indicating clearer data requests. The integration also now exposes a new Time Range option, which allows you to quickly select date ranges.
-
Enhancement: The GraphQL API includes a
requiresMetricTimeparameter to better handle metrics that must be grouped by time. (Certain metrics defined in MetricFlow can't be looked at without a time dimension). -
Enhancement: Enable querying metrics with offset and cumulative metrics with the time dimension name, instead of
metric_time. Issue #1000- Enable querying
metric_timewithout metrics. Issue #928
- Enable querying
-
Enhancement: Added support for consistent SQL query generation, which enables ID generation consistency between otherwise identical MF queries. Previously, the SQL generated by
MetricFlowEnginewas not completely consistent between identical queries. Issue 1020 -
Fix: The Tableau Connector returns a date filter when filtering by dates. Previously it was erroneously returning a timestamp filter.
-
Fix: MetricFlow now validates if there are
metrics,group by, orsaved_queryitems in each query. Previously, there was no validation. Issue 1002 -
Fix: Measures using
join_to_timespinein MetricFlow now have filters applied correctly after time spine join. -
Fix: Querying multiple granularities with offset metrics:
- If you query a time offset metric with multiple instances of
metric_time/agg_time_dimension, only one of the instances will be offset. All of them should be. - If you query a time offset metric with one instance of
metric_time/agg_time_dimensionbut filter by a different one, the query will fail.
- If you query a time offset metric with multiple instances of
-
Fix: MetricFlow prioritizes a candidate join type over the default type when evaluating nodes to join. For example, the default join type for distinct values queries is
FULL OUTER JOIN, however, time spine joins requireCROSS JOIN, which is more appropriate. -
Fix: Fixed a bug that previously caused errors when entities were referenced in
wherefilters.
January 2024
-
New: New metric type that allows you to measure conversion events. For example, users who viewed a web page and then filled out a form. For more details, refer to Conversion metrics.
-
New: Instead of specifying the fully qualified dimension name (for example,
order__user__country) in the group by or filter expression, you now only need to provide the primary entity and dimensions name, likeuser__county. -
New: You can now query the saved queries you've defined in the dbt Semantic Layer using Tableau, GraphQL API, JDBC API, and the dbt Cloud CLI.
-
Enhancement: The YAML spec parameter
labelis now available for Semantic Layer metrics in JDBC and GraphQL APIs. This means you can conveniently uselabelas a display name for your metrics when exposing them. -
Enhancement: Added support for
create_metric: truefor a measure, which is a shorthand to quickly create metrics. This is useful in cases when metrics are only used to build other metrics. -
Enhancement: Added support for Tableau parameter filters. You can use the Tableau connector to create and use parameters with your dbt Semantic Layer data.
-
Enhancement: Added support to expose
exprandaggfor Measures in the GraphQL API. -
Enhancement: You have improved error messages in the command line interface when querying a dimension that is not reachable for a given metric.
-
Enhancement: You can now query entities using our Tableau integration (similar to querying dimensions).
-
Enhancement: A new data source is available in our Tableau integration called "ALL", which contains all semantic objects defined. This has the same information as "METRICS_AND_DIMENSIONS". In the future, we will deprecate "METRICS_AND_DIMENSIONS" in favor of "ALL" for clarity.
-
Fix: Support for numeric types with precision greater than 38 (like
BIGDECIMAL) in BigQuery is now available. Previously, it was unsupported so would return an error. -
Fix: In some instances, large numeric dimensions were being interpreted by Tableau in scientific notation, making them hard to use. These should now be displayed as numbers as expected.
-
Fix: We now preserve dimension values accurately instead of being inadvertently converted into strings.
-
Fix: Resolved issues with naming collisions in queries involving multiple derived metrics using the same metric input. Previously, this could cause a naming collision. Input metrics are now deduplicated, ensuring each is referenced only once.
-
Fix: Resolved warnings related to using two duplicate input measures in a derived metric. Previously, this would trigger a warning. Input measures are now deduplicated, enhancing query processing and clarity.
-
Fix: Resolved an error where referencing an entity in a filter using the object syntax would fail. For example,
{{Entity('entity_name')}}would fail to resolve.